TITLE: Splitting a large woodland survey plot into 1 ha subdivisions
DATE: 2021-03-20
AUTHOR: John L. Godlee
====================================================================
In SEOSAW we have a few very large woodland monitoring plots. Six
25 ha plots in Republic of Congo, a 10 ha plot in the Democratic
Republic of Congo, and a 4 ha plot in South Africa. SEOSAW
advocates for using 1 ha square plots (100x100 m) in most cases, as
do many other similar ecological plot networks, because they are
big enough to be linked to remote sensing data, and big enough to
include what is normally a representative sample of the woodland.
[SEOSAW]:
https://seosaw.github.io
To increase the usefulness of the very large plots, we wanted to
split them up into 1 ha square subdivisions, and attribute stems to
each of these subdivisions based on stem location.
Here is the R function I wrote to split the plots:
#' Split large plots into 1 hectare squares
#'
#' @param x dataframe of stem measurements
#' @param plot_data dataframe of plot measurements
#' @param dims named character vector of length 2, specifying
the relationship
#' between the xy stem grid coordinate system and the plot
dimensions, i.e.
#' does the x axis run along the plot length, or the plot
width measurement
#' @param xy_zero_corner either "sw", "nw", "ne", "se",
specifying the corner
#' of the grid coordinate system origin (0,0)
#' @param x_direction either "ew" (east-west) or "ns"
(north-south), specifying
#' the direction of the x axis on the grid coordinate
system from the
#' origin corner
#' @param subplot_size the length and width of square subplots,
e.g. for 1 ha,
#' 100
#'
#' @return list:
#' 1) updated dataframe of stem measurements with added
\code{subdiv_id} to
#' show which subdivision each stem belongs to.
#' 2) sf dataframe of approximated subplot polygons and
their centres.
#' 3) updated dataframe of plot measurements with added
\code{subdiv} to
#' show whether a plot has been subdivided, and
\code{subdiv_id} to
#' identify new rows which are subdivided plots
#'
#' @details This function will only split a plot if it is
rectangular and the
#' area can be divided into 1 hectare squares without
remainder.
#'
#' @examples
#'
#'
#' @export
#'
largePlotSplit <- function(x, plot_data, polys, stem_plot_id =
"plot_id",
plot_plot_id = stem_plot_id, polys_plot_id = stem_plot_id,
dims = c("plot_length" = "x_grid", "plot_width" = "y_grid"),
xy_zero_corner = "sw", x_direction = "ew", subplot_size =
100) {
# Check parameter specified correctly
stopifnot(!any(is.na(names(dims))) & !is.null(names(dims)) &
length(dims)==2)
stopifnot(xy_zero_corner %in% c("sw", "se", "nw", "ne"))
stopifnot(x_direction %in% c("ns", "ew"))
# Subset plots which are the right dimensions to split and
which contain xy grid coords
plots_fil <- plot_data[
!is.na(plot_data[[names(dims)[1]]]) &
plot_data[[names(dims)[1]]] %% 100 == 0 &
plot_data[[names(dims)[1]]] %/% 100 >=2 &
!is.na(plot_data[[names(dims)[2]]]) &
plot_data[[names(dims)[2]]] %% 100 == 0 &
plot_data[[names(dims)[2]]] %/% 100 >=2 &
plot_data[[plot_plot_id]] %in%
unique(x[!is.na(x[[dims[1]]]) & !is.na(x[[dims[2]]]),
stem_plot_id])
,]
# Subset stems by plot IDs
x_fil <- x[x[[stem_plot_id]] %in% plots_fil[[plot_plot_id]],]
# Split stem measurements by plot
x_split <- split(x_fil, x_fil[[stem_plot_id]])
# For each plot:
plot_out <- lapply(seq_along(x_split), function(y) {
# New object, easier to work with
x_split_iso <- as.data.frame(x_split[[y]])
# Get plot ID
plot_id <- unique(x_split_iso[[stem_plot_id]])
# Throw warning if any stems not matched
no_coords <- which(is.na(x_split_iso[[dims[1]]]) |
is.na(x_split_iso[[dims[2]]]))
if (length(no_coords) > 0) {
warning(plot_id, ": discarded ", length(no_coords),
" stems with no XY grid coordinates")
}
x_split_fil <- x_split_iso[-no_coords,]
# Define bins per plot
cut_length <- plots_fil[plots_fil[[plot_plot_id]] ==
plot_id,names(dims)[1]] %/% subplot_size
cut_width <- plots_fil[plots_fil[[plot_plot_id]] ==
plot_id,names(dims)[2]] %/% subplot_size
bin_length <- seq(0, cut_length * subplot_size, by =
subplot_size)
bin_width <- seq(0, cut_width * subplot_size, by =
subplot_size)
# Classify each grid point by bins
x_split_fil$length_bin <- cut(x_split_fil[[dims[1]]],
bin_length)
x_split_fil$width_bin <- cut(x_split_fil[[dims[2]]],
bin_width)
# Get factor labels
length_bin_labels <- levels(x_split_fil$length_bin)
width_bin_labels <- levels(x_split_fil$length_bin)
# Deal with values slightly outside bins
# Length
poss_fix_length <-
x_split_fil[is.na(x_split_fil$length_bin) &
!is.na(x_split_fil[[dims[1]]]), dims[1]]
if (length(poss_fix_length) > 0) {
bin_length_close <- closestMatch(bin_length,
unlist(poss_fix_length))
bin_length_labs <- sapply(bin_length_close, function(i) {
if (i == min(bin_length)) {
length_bin_labels[1]
} else {
length_bin_labels[which(i == bin_length) -1]
}
})
x_split_fil[
is.na(x_split_fil$length_bin) &
!is.na(x_split_fil[[dims[1]]]), "length_bin"] <-
bin_length_labs
}
# Width
poss_fix_width <- x_split_fil[is.na(x_split_fil$width_bin)
&
!is.na(x_split_fil[[dims[2]]]), dims[2]]
if (length(poss_fix_width) > 0) {
bin_width_close <- closestMatch(bin_width,
unlist(poss_fix_width))
bin_width_labs <- sapply(bin_width_close, function(i) {
if (i == min(bin_width)) {
width_bin_labels[1]
} else {
width_bin_labels[which(i == bin_width)-1]
}
})
x_split_fil[
is.na(x_split_fil$width_bin) &
!is.na(x_split_fil[[dims[2]]]), "width_bin"] <-
bin_width_labs
}
# For each unique combination of bins, make a subplot, with
name
y_split <- split(x_split_fil, list(x_split_fil$length_bin,
x_split_fil$width_bin))
poss_subsets <- paste0(plot_id, "_S", seq(length(y_split)))
x_split_fil <- do.call(rbind, lapply(seq_along(y_split),
function(z) {
if (nrow(y_split[[z]]) > 0) {
y_split[[z]]$subdiv_id <- poss_subsets[z]
y_split[[z]]
}
}))
# Filter polygons to current plot ID
polys_fil <- polys[polys[[polys_plot_id]] == plot_id,]
# Extract corners as dataframe
polys_points <-
as.data.frame(sf::st_coordinates(polys_fil)[1:4,1:2])
# Get UTM zone of corners
utm_string <- UTMProj4(latLong2UTM(mean(polys_points[,1]),
mean(polys_points[,2])))
# Convert polygons to UTM
polys_utm <- sf::st_transform(polys_fil, utm_string)
# Convert UTM polygons to points
points_utm <- sf::st_cast(polys_utm, "POINT", warn =
FALSE)[1:4,]
# Extract coordinates as dataframe
coords_utm <-
as.data.frame(sf::st_coordinates(points_utm)[1:4,1:2])
# Get zero and bearing point
nw_outer <- sf::st_sfc(sf::st_point(
x = c(mean(coords_utm$X) - 1000, mean(coords_utm$Y) +
1000)))
ne_outer <- sf::st_sfc(sf::st_point(
x = c(mean(coords_utm$X) + 1000, mean(coords_utm$Y) +
1000)))
sw_outer <- sf::st_sfc(sf::st_point(
x = c(mean(coords_utm$X) - 1000, mean(coords_utm$Y) -
1000)))
se_outer <- sf::st_sfc(sf::st_point(
x = c(mean(coords_utm$X) + 1000, mean(coords_utm$Y) -
1000)))
if (xy_zero_corner == "sw") {
match_point <- sw_outer
other_point <- nw_outer
} else if (xy_zero_corner == "nw") {
match_point <- nw_outer
other_point <- sw_outer
} else if (xy_zero_corner == "ne") {
match_point <- ne_outer
other_point <- se_outer
} else if (xy_zero_corner == "se") {
match_point <- se_outer
other_point <- ne_outer
}
# Set CRS
sf::st_crs(other_point) <- sf::st_crs(points_utm)
sf::st_crs(match_point) <- sf::st_crs(points_utm)
# Get xy zero and opposite corner
xy_zero <- points_utm[sf::st_nearest_feature(match_point,
points_utm),]
xy_1 <- points_utm[sf::st_nearest_feature(other_point,
points_utm),]
# Convert to WGS for geosphere compatibility
xy_zero_wgs <- sf::st_coordinates(sf::st_transform(xy_zero,
4326))
xy_1_wgs <- sf::st_coordinates(sf::st_transform(xy_1, 4326))
# Get bearing between points
xy_bearing <- geosphere::bearing(xy_zero_wgs, xy_1_wgs)
# Make grid of 1 ha plots
bbox_grid <- cbind(x = c(0, 0, max(bin_length),
max(bin_length), 0),
y = c(0, max(bin_width), max(bin_width), 0, 0))
bbox_sf <- sf::st_polygon(list(bbox_grid))
polys_grid <- sf::st_make_grid(bbox_sf, cellsize =
subplot_size)
sf::st_crs(polys_grid) <- sf::st_crs(points_utm)
# Rotate to angle and move to centre of original plot
cent <- sf::st_centroid(sf::st_combine(points_utm))
grid_cent <- sf::st_centroid(sf::st_combine(polys_grid))
angle <- NISTunits::NISTdegTOradian(xy_bearing)
polys_rot <- (polys_grid - grid_cent) * rot(angle) * 1 +
cent
sf::st_crs(polys_rot) <- sf::st_crs(cent)
# Set order of subset IDs
byrow <- ifelse(x_direction == "ns", FALSE, TRUE)
if (xy_zero_corner %in% c("se", "nw")) {
ord <- cut_width:1
} else {
ord <- 1:cut_width
}
if (xy_zero_corner %in% c("sw", "nw")) {
subdiv_ids <- poss_subsets
} else {
subdiv_ids <- rev(poss_subsets)
}
# Create matrix of subset IDs
subset_mat <- matrix(subdiv_ids,
nrow = cut_width, ncol = cut_length, byrow = byrow)[ord,]
# Apply matrix to name polygons
polys_rot_sf <- sf::st_sf(geometry = polys_rot,
plot_id = plot_id,
subdiv_id = as.vector(t(subset_mat)))
polys_rot_wgs <- sf::st_transform(polys_rot_sf, 4326)
names(polys_rot_wgs)[1] <- plot_plot_id
# Remove bins
x_split_fil_clean <- x_split_fil[,!(names(x_split_fil) %in%
c("length_bin", "width_bin"))]
# Add back in stems which had no grid coords
x_split_iso$subdiv_id <- NA_character_
x_split_out <- rbind(x_split_fil_clean,
x_split_iso[no_coords,names(x_split_fil_clean)])
# Return list
return(list(x_split_out, polys_rot_wgs))
})
# Bind all stems together
stems_out <- do.call(rbind, lapply(plot_out, "[[", 1))
# Bind back in stems from plots which weren't split
if (nrow(x[!x[[stem_plot_id]] %in%
plots_fil[[plot_plot_id]],]) > 0) {
stems_non <- x[!x[[stem_plot_id]] %in%
plots_fil[[plot_plot_id]],]
stems_non$subdiv_id <- NA_character_
stems_all <- rbind(stems_out, stems_non[,names(stems_out)])
} else {
stems_all <- stems_out
}
# Bind all polygons
polys_out <- do.call(rbind, lapply(plot_out, "[[", 2))
# Add centres to polygons
centres <- suppressWarnings(
as.data.frame(st_coordinates(st_centroid(polys_out))))
names(centres) <- c("longitude_of_centre",
"latitude_of_centre")
polys_out <- cbind(polys_out, centres)
# Add subdiv column to plots table
plot_data$subdiv <- ifelse(plot_data[[plot_plot_id]] %in%
polys_out[[plot_plot_id]], TRUE, FALSE)
# Add subdivided columns to plots data
subdiv_out <- merge(st_drop_geometry(polys_out),
plot_data[,!names(plot_data) %in% c("longitude_of_centre",
"latitude_of_centre")],
by = plot_plot_id, all.x = TRUE)
subdiv_out[subdiv_out$subdiv_id %in% polys_out$subdiv_id,
"plot_area"] <- subplot_size * subplot_size / 10000
subdiv_out[subdiv_out$subdiv_id %in% polys_out$subdiv_id,
"plot_length"] <- subplot_size
subdiv_out[subdiv_out$subdiv_id %in% polys_out$subdiv_id,
"plot_width"] <- subplot_size
subdiv_out[subdiv_out$subdiv_id %in% polys_out$subdiv_id,
"plot_perimeter"] <- subplot_size * 4
subdiv_out[subdiv_out$subdiv_id %in% polys_out$subdiv_id,
"subdiv"] <- FALSE
plot_data$subdiv_id <- NA_character_
plot_data_out <- rbind(plot_data,
subdiv_out[,names(plot_data)])
# Return list of output
return(list(stems_all, polys_out, plot_data_out))
}
Hopefully the comments explain everything, but this function is
quite complicated, and I'm proud of it, so I'll describe it step by
step.
1. Find which plots are suitable for splitting. Plots must be
rectangular, larger than 2 ha, the plot length and width must be
divisible without remainder into 100 m lengths, and there must be
at least one stem in the plot with grid coordinates. Then, for each
suitable plot:
2. Assign each stem to 100 m bins in the X and Y direction, using
cut().
3. For stems with grid coordinates slightly outside the plot
boundary (this is often a problem when converting from lat-long to
grid coordinates), find the closest bin, using a separate function
called closestMatch(), see below for more details.
4. For each unique combination of bins, make a subdivision ID, and
assign names based on the direction of stem coordinate progression
and which corner the stem coordinate system originates from,
referencing the x_direction and xy_zero_corner function parameters.
5. Make a grid of 1 ha square polygons from the plot dimensions,
using sf::st_make_grid(). Then rotate the polygon grid and move to
the centre of the existing plot polygon.
6. Name each of the subdivision polygons with the subdiv_id used
for the stems.
7. Return a dataframe of stem measurements with subdiv_id values
for each stem, and an {sf} object with the subdivision polygons and
their centres.
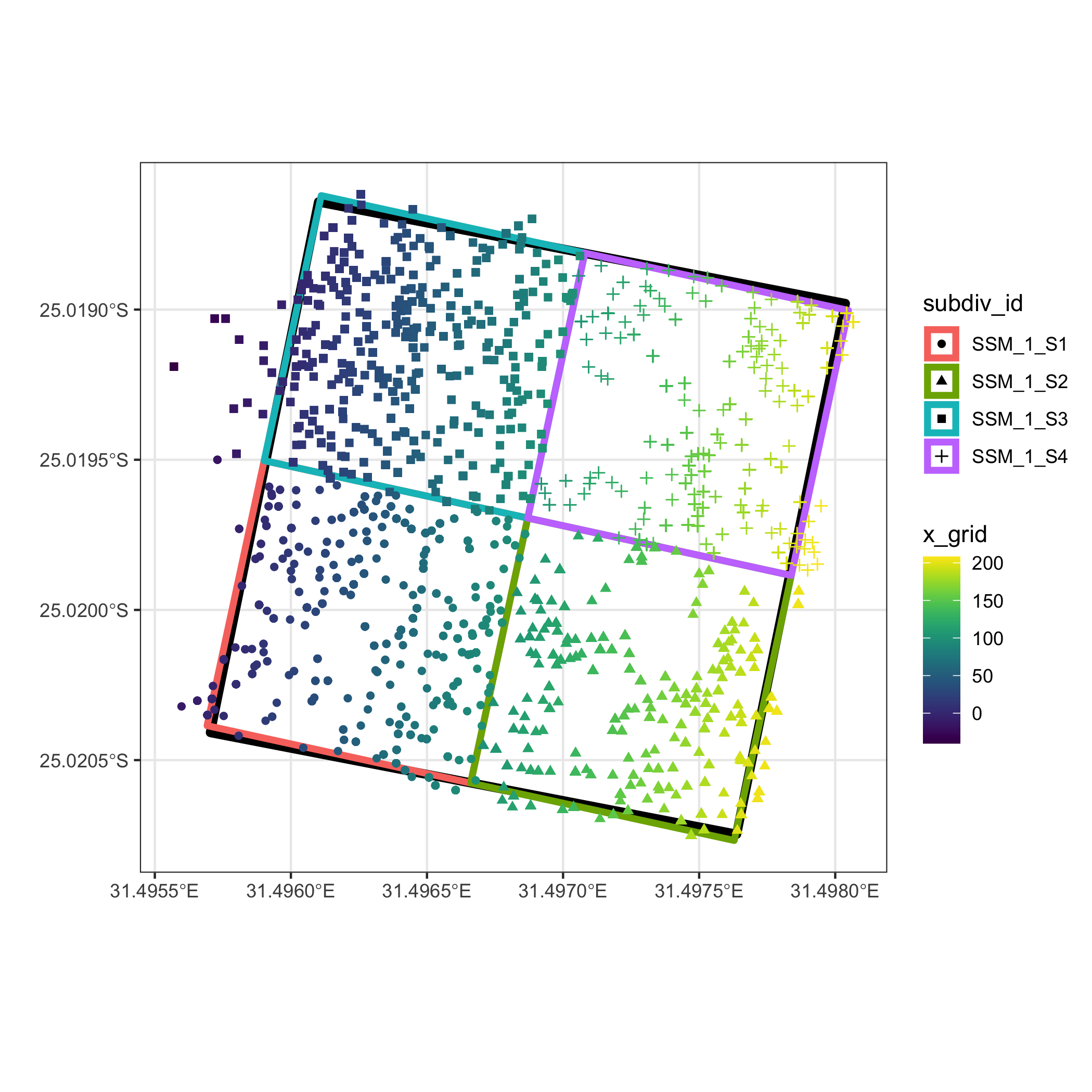
The plot below illustrates a 4 ha plot that has been split into
four 1 ha subdivisions using the above methods.
library(ggplot2)
library(ggnewscale)
library(viridis)
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = polys_sf, colour = "black", size = 2, fill =
NA) +
geom_sf(data = out[[2]], aes(colour = subdiv_id), size = 1.5,
fill = NA) +
new_scale_colour() +
geom_point(data = out[[1]],
aes(x = longitude, y = latitude, colour = x_grid, shape =
subdiv_id)) +
scale_colour_viridis() +
theme_bw() +
labs(x = "", y = "")
Finally, here is the closestMatch() function:
#' Find closest match in a vector
#'
#' @param x numeric vector
#' @param y vector of numeric values, each of which be matched
with the closest
#' value in \code{x}
#'
#' @return numeric vector of values of \code{x} that are
closest to each
#' element of \code{y}
#'
#' @keywords internal
#' @noRd
#'
closestMatch <- function(x, y) {
unlist(lapply(y, function(i) {
x[which(abs(x-i) == min(abs(x-i)))]
}))
}